Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (1): 9-16.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.01.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-likecells induced by P53 specific inhibitor p-fifty three inhibitor-alpha
Yan Xue-bo1, Hu Zhao-hui1, Du Yun-hua1, Lü An-lin2, Xing Yu-jie2
- 1 Department of Cardiology, No.154 Central Hospital of Chinese PLA, Xinyang 464000, Henan Province, China
2 Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University of Chinese PLA, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2012-04-01Revised:2012-04-18Online:2013-01-01Published:2013-01-01 -
Contact:Lü An-lin, Doctor, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China lvanlin@fmmu.edu.cn -
About author:Master, Attending physician, Department of Cardiology, No.154 Central Hospital of Chinese PLA, Xinyang 464000, Henan Province, China yanxuebo1979@gmail.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Xue-bo, Hu Zhao-hui, Du Yun-hua, Lü An-lin, Xing Yu-jie. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-likecells induced by P53 specific inhibitor p-fifty three inhibitor-alpha[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(1): 9-16.
share this article
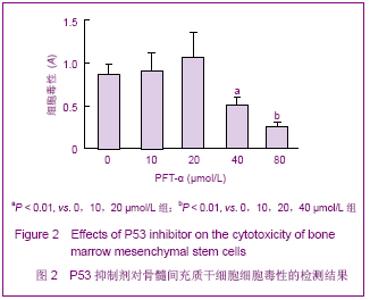
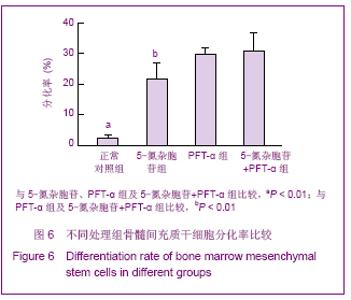
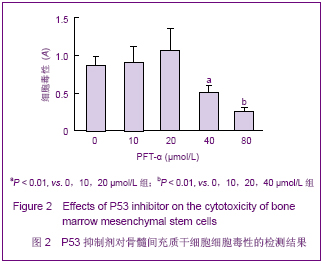
2.2 不同浓度PFT-α对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响 实验结果显示,当PFT-α浓度≤20 μmol/L时,对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖有一定促进作用,而当其浓度达到 40 μmol/L时,PFT-α则可明显抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,与0,10,20 μmol/L PFT-α组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。当浓度达到80 μmol/L时,PFT-α显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,与0,10,20,40 μmol/L PFT-α组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见图2。实验结果显示PFT-α浓度≤20 μmol/L时对骨髓间充质干细胞无细胞毒性,对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖有一定促进作用,而当其浓度高于40 μmol/L则具有明显的细胞毒副作用。"

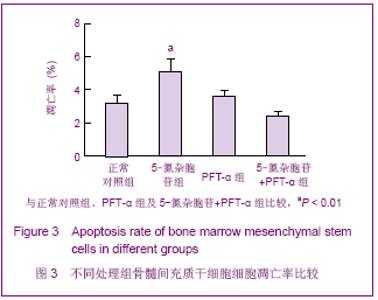
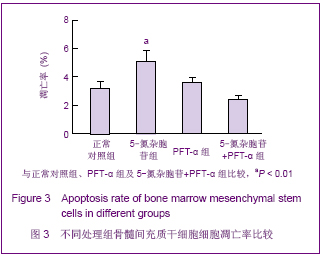
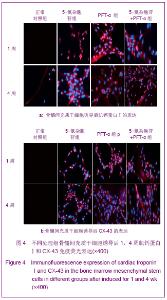
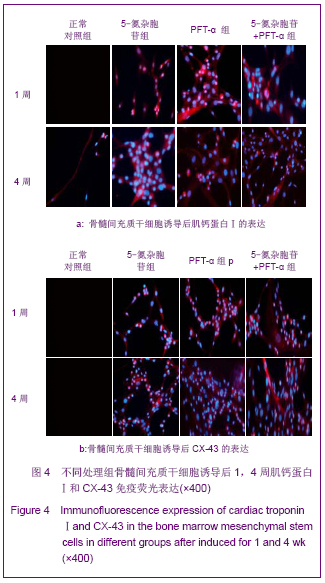
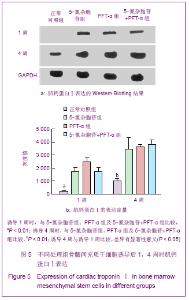
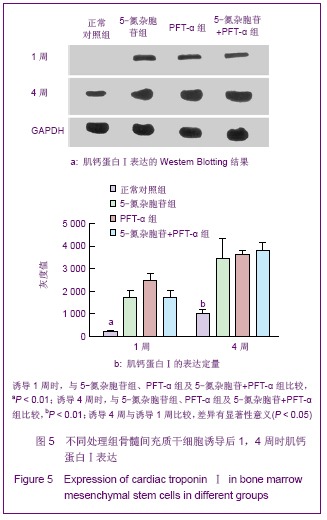
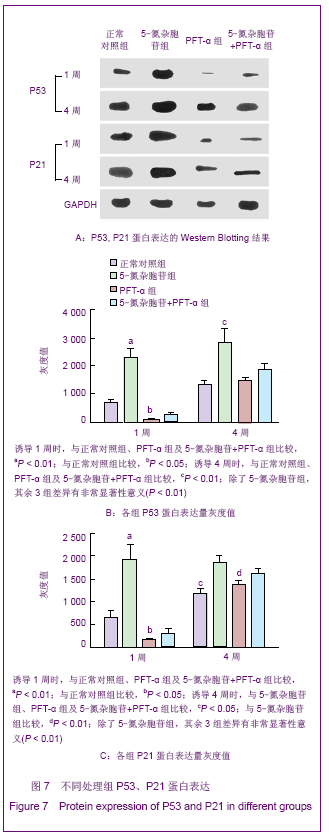
2.6 不同处理组P53、P21蛋白表达 见图7。 诱导1周时,5-氮杂胞苷组P53、P21表达最强,PFT-α组几乎不表达,5-氮杂胞苷组与其余3组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01),PFT-α组与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),PFT-α和5-氮杂胞苷+PFT-α组间差异无显著性意义。 诱导4周时,5-氮杂胞苷组仍强表达,其余3组表达较1周时有所增强,5-氮杂胞苷组、PFT-α组、混合组与对照组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),5-氮杂胞苷组与PFT-α组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),其余组间差异无显著性意义。 PFT-α组、混合组组内诱导4周时P53、P21表达量与1周时比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),但5-氮杂胞苷组前后差异无显著性意义。"
| [1] Elizabeth GN. Cardiovascular disease. New England J Med. 2003;349:60-72.[2] Cao F, Sun DD, Li CX, et al. Long-term myocardial functional improvement after autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells transplantation in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: 4 years follow-up. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30(16):1986-1994.[3] Deng W, Obrocka M, Fischer I, et al. In vitro differentiation of human marrow stromal cells into early progenitors of neural cells by conditions that increase intracellular cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282(1): 148-152.[4] Wakitani S, Saito T, Caplan AI. Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 1995;18:1417-1426.[5] Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, et al. Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(5):697-705. [6] Hong H, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, et al. Suppression of induced pluripotent stem cell generation by the p53-p21 pathway. Nature. 2009;460: 1132-1136.[7] Armesilla DA, Elvira G, Silva A. p53 regulates the proliferation, differentiation and spontaneous transformation of mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315: 3598-3610.[8] Pulukuri SM, Rao JS. Activation of p53/p21Waf1/Cip1 pathway by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine inhibits cell proliferation, induces pro-apoptotic genes and mitogen-activated protein kinases in human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2005;26(4): 863-871.[9] Zhu WG, Hileman T, Ke Y, et al. 5-Aza-2,-deoxycytidine Activates the p53/p21Waf1/Cip1 Pathway to Inhibit Cell Proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(15): 15161-15166.[10] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[11] Bergmann O, Bhardwaj RD, Bernard S, et al. Evidence for Cardiomyocyte Renewal in Humans. Science. 2009; 324 (5923): 98 -102.[12] Li X,Yu X, Lin Q, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into functional cardiac phenotypes by cardiac microenvironment. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42(2):295-303. [13] Wang JS, Shunr Tim D, Galipeeall J, et al. Marrou Stramol cells for cellular Cardiomyoplasty :feasibillty and potential dinical advantages. Thorae Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;120(62): 999-1005.[14] Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, et al. Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation. 2002;106 (15):1913-1918.[15] Janssens S, Dubois C, Bogaert J, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived stem-cell transfer in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction:double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006;367(9505): 113-121. [16] Wollert KC, Meyer GP, Lotz J, et al. Intracoronary autologous bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: The BOOST randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429) :141-148.[17] Lago N, Trainini J, Christen A, et al. Mononuclear bone marrow stem cells implant as an alternative treatment in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(4 Suppl. A):1A-384A.[18] Wang J, Xie X, He H, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of autologous mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for dilated cardiomyopathy. Chin J Cardiol. 2006;34(2):107-111. [19] Komarova EA, Gudkov AV. Suppression of p53: a new app roach to overcome side effects of antitumor therapy. Biochemistry (Mosc).2000;65:41-48.[20] Schneider SR, Diab AM, Rohrbeck A, et al. 5-aza-Cytidine is a potent inhibitor of DNA Methyltransferase 3a and induces apoptosis in HCT-116 colon cancer cells via Gadd45- and p53-Dependent Mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005; 312(2):525-536.[21] Yan XB, Lü AL, Liu BW, et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(14):2482-2486.燕学波,吕安林,刘博武,等. P53-P21蛋白通路对5-氮杂胞苷诱导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(14):2482-2486.[22] Levine AJ, Finlay CA, Hinds PW. P53 is a Tumor Suppressor Gene. Cell. 2004;116:67-69.[23] Schuler M, Green DR. Transcription, apoptosis and P53: catch-22. Trends Genet. 2005;21(3): 182-187.[24] Xuwan L, Chu CC, Jinping G, et al. Pifithrin-α protects against doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and acute cardiotoxicity in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286: 933-939.[25] Shave R, Baggish A, George K, et al. Exercise-induced cardiac troponin elevation: evidence, mechanisms, and implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(3):169-176. [26] Janczarska K, Kie?-Wilk B, Leszczyńska-Go?abek I, et al. The role of connexin 43 in preconditioning. Impact on mitochondrial function. Kardiol Pol. 2010;68(1):91-96. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [13] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||